Berberine is a bioactive compound found in several plants, including goldenseal, barberry, Oregon grape, and tree turmeric. Known for its vibrant yellow color, this alkaloid has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine. In recent years, berberine has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, particularly in managing blood sugar, improving heart health, and supporting weight loss. This article explores the usage, benefits, and important points about berberine in detail.
What is Berberine?
- Definition: Berberine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound extracted from the roots, rhizomes, and stems of certain plants.
- Sources: Found in plants like Berberis vulgaris (barberry), Hydrastis canadensis (goldenseal), and Coptis chinensis (Chinese goldthread).
- Appearance: Bright yellow compound, often used as a natural dye.
- Historical Use: Traditionally used in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic properties.
How Does Berberine Work?
- Mechanism of Action: Berberine activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme that regulates metabolism, promoting glucose uptake and fat breakdown.
- Cellular Impact: Influences multiple pathways, including insulin signaling, mitochondrial function, and gut microbiota modulation.
- Bioavailability: Berberine has low bioavailability, meaning it’s poorly absorbed in the gut. Combining it with compounds like milk thistle or taking specialized formulations (e.g., berberine HCl) can enhance absorption.
Health Benefits of Berberine:
Berberine’s therapeutic potential has been studied extensively, with research highlighting its benefits for various health conditions. Below are the key benefits:
- Blood Sugar Regulation
- Effectiveness: Comparable to some diabetes medications, berberine can lower blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity.
- Mechanism: Enhances glucose uptake in cells and reduces glucose production in the liver.
- Studies: A 2019 meta-analysis found berberine significantly reduced fasting blood glucose and HbA1c in type 2 diabetes patients.
- Heart Health
- Cholesterol Management: Lowers LDL (bad cholesterol) and triglycerides while increasing HDL (good cholesterol).
- Blood Pressure: May reduce blood pressure by improving vascular function.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Reduces the risk of heart disease by decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Weight Loss Support
- Metabolic Boost: Activates AMPK, which promotes fat burning and reduces fat storage.
- Appetite Regulation: May influence hormones like leptin, helping control appetite.
- Research: Studies show modest weight loss in obese individuals taking berberine supplements.
- Gut Health and Microbiota
- Antimicrobial Properties: Fights harmful gut bacteria, fungi, and parasites, promoting a balanced microbiome.
- Digestive Benefits: May alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive disorders.
- Prebiotic Effects: Encourages the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
- Reduces Inflammation: Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines, potentially benefiting conditions like arthritis.
- Antioxidant Properties: Neutralizes free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- Potential Anticancer Properties
- Emerging Research: Preliminary studies suggest berberine may inhibit cancer cell growth in certain types (e.g., colon, breast, and liver cancer).
- Mechanism: Induces apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth pathways.
Clinical Data on Berberine’s Effects:
The table below summarizes key findings from clinical studies on berberine’s impact on health parameters.
| Study Year | Condition | Dosage (mg/day) | Duration | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Type 2 Diabetes | 1000–1500 | 12 weeks | Reduced fasting blood glucose by 20%, HbA1c by 12% compared to placebo. |
| 2015 | High Cholesterol | 1000 | 8 weeks | Lowered LDL cholesterol by 15%, triglycerides by 18%, increased HDL by 7%. |
| 2018 | Obesity | 1500 | 12 weeks | Average weight loss of 2.3 kg; reduced BMI by 1.2 points in obese participants. |
| 2020 | IBS | 800 | 8 weeks | Improved IBS symptoms (bloating, pain) in 60% of participants vs. 35% in placebo. |
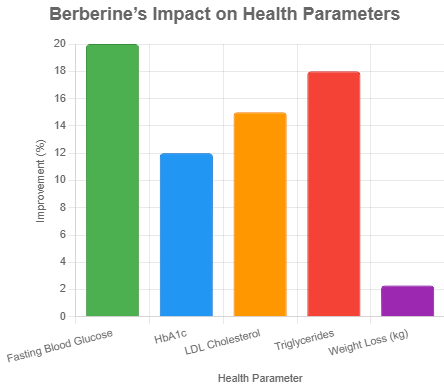
Chart: Berberine’s Impact on Health Parameters
The chart below illustrates the percentage improvement in key health markers based on clinical studies.
Common Uses of Berberine:
- Diabetes Management: Used as a natural supplement to control blood sugar in type 2 diabetes.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Improves insulin resistance and hormonal balance in women with PCOS.
- Cholesterol Management: Taken to lower cholesterol levels and support cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Incorporated into weight loss regimens to enhance metabolism.
- Infections: Used for its antimicrobial properties to treat bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections.
- Digestive Health: Taken to improve gut health and alleviate symptoms of IBS or SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth).
Dosage and Administration:
- Typical Dosage: 500–1500 mg per day, divided into 2–3 doses, taken with meals to improve absorption and reduce stomach upset.
- Forms: Available as capsules, tablets, or powders; berberine HCl is the most common form.
- Duration: Often taken for 8–12 weeks, followed by a break to prevent potential side effects from long-term use.
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare provider before starting berberine, especially if taking medications or managing chronic conditions.
Safety and Side Effects:
- Common Side Effects: Mild gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, constipation, or stomach cramps.
- Drug Interactions: May interact with medications like metformin, statins, or blood thinners. Consult a doctor if on prescription drugs.
- Contraindications: Not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women due to limited safety data.
- Low Blood Sugar Risk: Can cause hypoglycemia in some individuals, particularly when combined with diabetes medications.
Important Considerations:
- Quality of Supplements: Choose high-quality, third-party-tested berberine supplements to ensure purity and potency.
- Bioavailability Enhancement: Pairing berberine with milk thistle, piperine, or specialized formulations can improve absorption.
- Not a Replacement for Medication: Berberine should complement, not replace, prescribed treatments for conditions like diabetes or high cholesterol.
- Individual Response: Effects vary based on individual health, dosage, and consistency of use.
Who Should Consider Berberine?
- Individuals with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes seeking natural blood sugar support.
- People with high cholesterol or cardiovascular risk factors.
- Those struggling with weight management or metabolic syndrome.
- Individuals with gut health issues like IBS or SIBO.
- Anyone interested in natural anti-inflammatory or antimicrobial supplements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is berberine safe for long-term use?
- Short-term use (8–12 weeks) is generally safe, but long-term safety is less studied. Take breaks and consult a healthcare provider.
- Can berberine replace diabetes medications?
- No, berberine should not replace prescribed medications but can be used as a complementary therapy under medical supervision.
- How quickly does berberine work?
- Effects on blood sugar or cholesterol may be noticeable within a few weeks, but consistent use for 1–3 months is often needed for significant results.
- Can berberine help with weight loss?
- Berberine may support modest weight loss by boosting metabolism and regulating appetite, but it’s not a magic solution.
Conclusion:
Berberine is a powerful natural compound with a wide range of potential health benefits, from blood sugar control to heart health and gut support. Its versatility and centuries-old use in traditional medicine make it a compelling option for those seeking natural health solutions. However, it’s crucial to use berberine responsibly, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to maximize benefits and minimize risks. Whether you’re managing a chronic condition or aiming to optimize your health, berberine may be a valuable addition to your wellness routine.


1 thought on “Berberine: Usage, Benefits, and Key Information”
Comments are closed.